Python 3 While 循环
While 在Python编程语言中,只要给定的条件为真,则循环语句重复执行一个目标语句。
语法
Python 编程语言中while循环的语法是
while expression:
statement(s)
这里,语句可以是单个语句或语句块。条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零值都为true。当条件为真时循环进行迭代。
当条件为假时,程序控制传递到紧跟在循环后面的那一行。
在 Python 中,在编程构造之后缩进相同数量的字符空格的所有语句都被视为单个代码块的一部分。Python 使用缩进作为分组语句的方法。
流程图
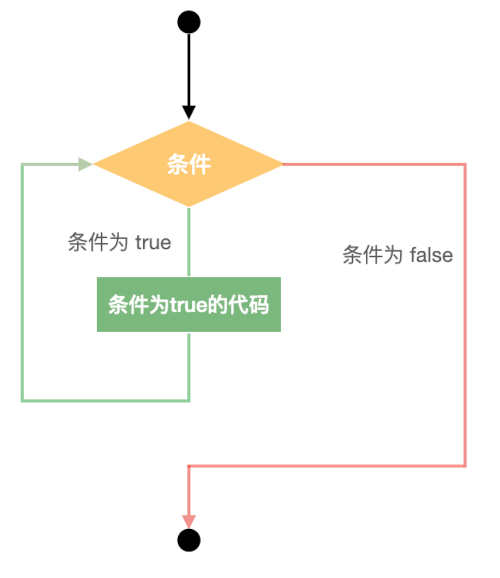
在这里,while 循环的关键在于循环可能永远不会运行。当条件被测试并且结果为假时,将跳过循环体并执行while循环之后的第一条语句。
示例
#!/usr/bin/python3
count = 0
while (count < 9):
print ('The count is:', count)
count = count + 1
print ("Good bye!")
代码执行结果如下:
The count is: 0
The count is: 1
The count is: 2
The count is: 3
The count is: 4
The count is: 5
The count is: 6
The count is: 7
The count is: 8
Good bye!
这里由打印和增量语句组成的块重复执行,直到计数不再小于 9。 每次迭代,显示索引计数的当前值,然后增加 1。
无限循环
如果条件永远不会变为 FALSE,则循环变为无限循环。使用 while 循环时必须小心,因为此条件可能永远不会解析为 FALSE 值。这会导致一个永无止境的循环。这样的循环称为无限循环。
无限循环在客户端/服务器编程中可能很有用,其中服务器需要连续运行,以便客户端程序可以在需要时与其进行通信。
#!/usr/bin/python3
var = 1
while var == 1 : # This constructs an infinite loop
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
print ("You entered: ", num)
print ("Good bye!")
执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 -
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
Enter a number :11
You entered: 11
Enter a number :22
You entered: 22
Enter a number :Traceback (most recent call last):
File "examples\test.py", line 5, in
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
KeyboardInterrupt
上面的示例进入无限循环,您需要使用 CTRL+C 退出程序。
在 While 循环中使用 else 语句
Python 支持将else语句与循环语句关联。
如果else语句与while循环一起使用,则在条件变为假时执行else语句。
以下示例说明了 else 语句与 while 语句的组合,该语句打印一个小于 5 的数字,否则执行 else 语句。
#!/usr/bin/python3
count = 0
while count < 5:
print (count, " is less than 5")
count = count + 1
else:
print (count, " is not less than 5")
代码执行结果如下:
0 is less than 5
1 is less than 5
2 is less than 5
3 is less than 5
4 is less than 5
5 is not less than 5
单一语句场景
与if语句语法类似,如果您的while子句仅包含一条语句,则它可能与 while 标题位于同一行。
这是单行 while子句的语法和示例-
#!/usr/bin/python3
flag = 1
while (flag): print ('Given flag is really true!')
print ("Good bye!")
最好不要尝试上面的示例,因为它会进入无限循环,您需要按 CTRL+C 键退出。
