C++中的魔方问题
本文将解释魔方问题、它的属性以及它使用 C++ 的实现。 让我们学习魔方问题来实现魔方。
魔方问题
魔方是正整数的二维数组,其中每一行、每一列和对角线的总和都相同。 求和常被称为Magic Sum,指的是每一行、每一列、每一对角线的总和是常数。
魔方的每个位置的整数值必须是唯一的。 如果 N 是魔方的大小,它可以包含从 1 到 N2 的整数。
以下公式计算幻数和。
魔方的大小将指示行数和列数。 如果 N 等于 3,则幻方将具有三行和三列。
现在,让我们用一个例子来解释魔术和。 假设N的值为3,则由上式可计算为:
在这里,15 是神奇的总和。 这意味着每列、每行和对角线之和应等于 15。
大小等于3的魔方如下图所示。
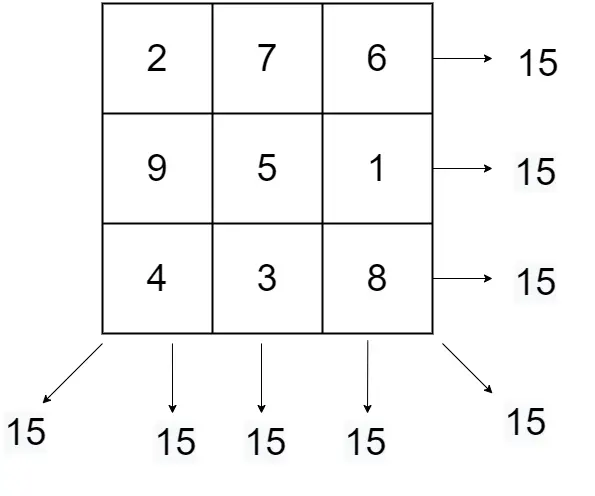
我们可以看到每一行、每一列、每一对角线的和都等于幻数和,而且每一项都是唯一的。
了解了幻方问题之后,现在我们来实现一下。
让我们将要实现的幻方的大小为 n。 然后,第一个值(即 1)存储在幻方中的位置(n/2,n-1)。
假设这个位置是 (i,j),那么下一个值将在位置 (i-1,j+1)。 这里我们假设每一行和每一列都有一个环绕(即,也称为圆圈时尚)。
魔方问题的条件
-
下一个值的位置由当前列号加 1 和当前行号减 1 来确定。
- 如果列的新位置变为 n,那么它将被包装为 0,因为列和行是循环的。
- 同样,如果乌鸦的新位置变成了-1,它就会被包裹到n-1。
- 假设新计算的位置已经包含一个值。 在这种情况下,当前行号将通过加 1 来更新,而当前列号将通过从中减去 2 来更新。
- 如果新计算出来的列号是n,行号是-1,那么更新的位置就是(0,n-2)。
C++中魔方的实现
在进入细节之前,让我们先看看下面的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// This function will generate an old-size magic square only.
void magicSquareGenerator(int s)
{
int magic_Square[s][s];
// This will initialize all locations of the magic square to 0
memset(magic_Square, 0, sizeof(magic_Square));
// here, r is the row index, and c is the column index for the first number
int r = s / 2;
int c = s - 1;
// generating magic square
for (int num = 1; num <= s * s;) {
if (r == -1 && c == s) // Third condition
{
c = s - 2;
r = 0;
}
else {
if (c == s)
c = 0;
if (r < 0)
r = s - 1;
}
if (magic_Square[r][c]) // second condition
{
c -= 2;
r++;
continue;
}
else
magic_Square[r][c] = num++;
c++;
r--; // 1st condition
}
// Print magic square
cout << "The Magic Square has:"<<s<<" rows and "<<s<<" columns.";
cout <<"\nThe Magic Sum is: "<< s * (s * s + 1) / 2 << ":\n";
for (r = 0; r < s; r++) {
for (c = 0; c < s; c++)
// displaying the magic square.
cout << setw(4) << magic_Square[r][c] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{ //Code expects only odd sizes
int s;
cout<<"Enter the size of the Magic Square: ";
cin>>s;
while(s%2==0){
cout<<"Plz Enter an odd number :"<<endl;
cout<<"Enter the size of the Magic Square: ";
cin>>s;
}
magicSquareGenerator(s);
return 0;
}
下面是对上述魔方程序的逐步解释。
- 值 1 的位置 = (3/2,3-1) = (1,2) = [1][2]。
- 值 2 的位置 = (1-1,2+1) = (1,2) = [1][2]。
- 值 3 的位置 = (0-1,0+1) = (3-1,1+1) = [2][1]。
-
值 4 的位置 = (2-1,1+1) = (1,2) = [1][2]。
- 由于 [1][2] 已经具有值 1,因此根据条件 2,新位置将为 (1+1,2-2) = [2][0]。
- 值 5 的位置 = (2-1,0+1) = (1,1) = [1][1]。
- 值 6 的位置 = (1-1,1+1) = (1,2) = [0][2]。
-
值 7 的位置 = (0-1,2+1) = (-1,3)
- 条件 3 成立,因此新位置将为 (0,3-2)=[0][1]。
- 值 8 的位置是 = (0-1,1+1) = (-1,2) = [2][2] 因为条件 1 行被换行。
- 值 9 的位置是 = (2-1,2+1) = (1,3) = [1][0] 因为条件 1 列被换行。
这是我们输入魔方 3 的大小时的输出。
Enter the size of the Magic Square: 3
The Magic Square has:3 rows and 3 columns.
The Magic Sum is: 15:
2 7 6
9 5 1
4 3 8
这是我们输入魔方 7 的大小时的输出。
Enter the size of the Magic Square: 7
The Magic Square has:7 rows and 7 columns.
The Magic Sum is: 175:
20 12 4 45 37 29 28
11 3 44 36 35 27 19
2 43 42 34 26 18 10
49 41 33 25 17 9 1
40 32 24 16 8 7 48
31 23 15 14 6 47 39
22 21 13 5 46 38 30
所提出算法的时间和空间复杂度为 $O(n^2)$。
相关文章
Arduino 复位
发布时间:2024/03/13 浏览次数:315 分类:C++
-
可以通过使用复位按钮,Softwarereset 库和 Adafruit SleepyDog 库来复位 Arduino。
Arduino 的字符转换为整型
发布时间:2024/03/13 浏览次数:181 分类:C++
-
可以使用简单的方法 toInt()函数和 Serial.parseInt()函数将 char 转换为 int。
Arduino 串口打印多个变量
发布时间:2024/03/13 浏览次数:381 分类:C++
-
可以使用 Serial.print()和 Serial.println()函数在串口监视器上显示变量值。

