Matplotlib 中 cla()、clf()和 close()方法之间的区别
matplotlib.pyplot.cla() 方法清除当前坐标轴,matplotlib.pyplot.clf() 方法清除当前图形,matplotlib.pyplot.close() 方法关闭整个窗口。
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=np.linspace(0,2*math.pi,100)
y1=np.sin(x)
y2=np.cos(x)
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,1)
ax[0].plot(x,y1)
ax[0].set_xlabel("x")
ax[0].set_ylabel("sinx")
ax[0].set_title("Plot of sinx")
ax[1].plot(x,y2)
ax[1].set_xlabel("x")
ax[1].set_ylabel("cosx")
ax[1].set_title("Plot of cosx")
fig.suptitle('Plot of sinx and cosx',fontsize=16)
fig.tight_layout(pad=3.0)
plt.show()
输出:
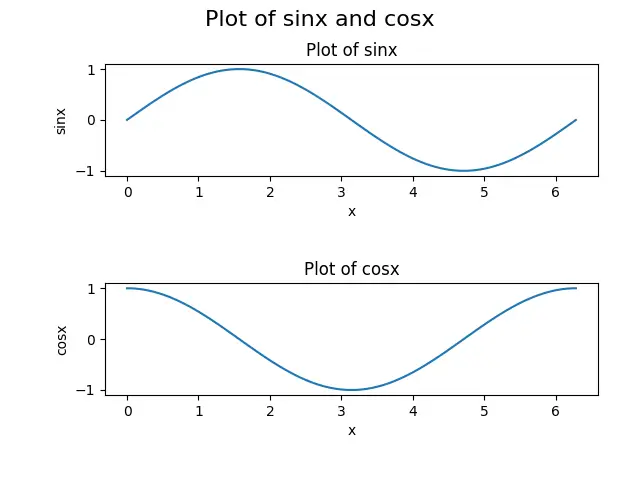
我们将用这个图来解释以下函数:cla()、clf() 和 close()。该图由一个图和两个子图组成,上排的子图是 sinx 函数的图,下排的子图表示 cosx 函数的图。
matplotlib.pyplot.cla()
matplotlib.pyplot.cla() 命令用于清除 Matplotlib 中的当前坐标轴。Axes 只是一个图的一部分,通常是一个子图及其细节。
例如:matplotlib.pyplot.cla()
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=np.linspace(0,2*math.pi,100)
y1=np.sin(x)
y2=np.cos(x)
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,1)
ax[0].plot(x,y1)
ax[0].set_xlabel("x")
ax[0].set_ylabel("sinx")
ax[0].set_title("Plot of sinx")
ax[1].plot(x,y2)
ax[1].set_xlabel("x")
ax[1].set_ylabel("cosx")
ax[1].set_title("Plot of cosx")
ax[1].cla()
fig.suptitle('Plot of sinx and cosx',fontsize=16)
fig.tight_layout(pad=3.0)
plt.show()
输出:
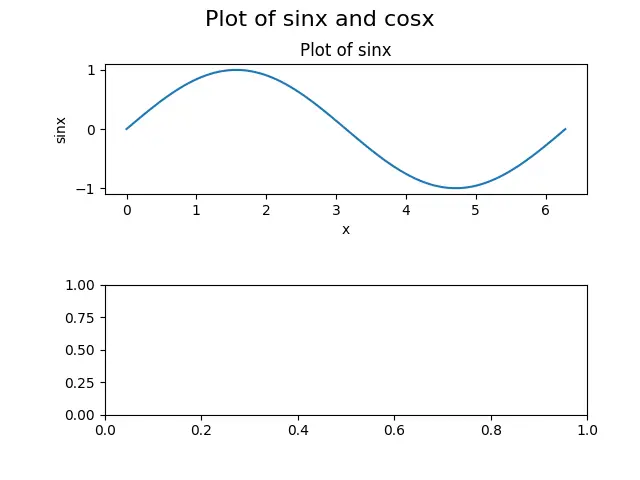
在这里,我们可以看到,cla() 方法清除了 ax[1] 轴,即子图的第二行。清除轴意味着删除子图及其细节,如 xlabel、ylabel 和 title;但是,轴 ax[0] 或顶部的子图没有被该方法改变,因为 cla() 只被 ax[1] 轴调用。
matplotlib.pyplot.cla()
matplotlib.pyplot.clf() 可以清除 Matplotlib 中的整个图。图形可以看作是一个画图的超集,由画图中的每一个细节组成,如子图、子轴、标题和图例。
例:matplotlib.pyplot.clf()
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=np.linspace(0,2*math.pi,100)
y1=np.sin(x)
y2=np.cos(x)
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,1)
ax[0].plot(x,y1)
ax[0].set_xlabel("x")
ax[0].set_ylabel("sinx")
ax[0].set_title("Plot of sinx")
ax[1].plot(x,y2)
ax[1].set_xlabel("x")
ax[1].set_ylabel("cosx")
ax[1].set_title("Plot of cosx")
fig.suptitle('Plot of sinx and cosx',fontsize=16)
fig.tight_layout(pad=3.0)
plt.clf()
plt.show()
输出:

在这里,我们可以看到 clf() 方法清除了绘图中的所有内容。这个过程包括了所有的坐标轴;但是,绘图窗口仍然存在,它可以被重新使用来生成其他的图形。
请注意,我们不能对每个轴使用clf()方法。
matplotlib.pyplot.close()
matplotlib.pyplot.close() 只是关闭了 Matplotlib 中的图窗口,我们在调用 plt.show() 方法时不会看到任何东西。
例:matplotlib.pyplot.close()
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=np.linspace(0,2*math.pi,100)
y1=np.sin(x)
y2=np.cos(x)
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,1)
ax[0].plot(x,y1)
ax[0].set_xlabel("x")
ax[0].set_ylabel("sinx")
ax[0].set_title("Plot of sinx")
ax[1].plot(x,y2)
ax[1].set_xlabel("x")
ax[1].set_ylabel("cosx")
ax[1].set_title("Plot of cosx")
fig.suptitle('Plot of sinx and cosx',fontsize=16)
fig.tight_layout(pad=3.0)
plt.close()
plt.show()
脚本不会产生任何输出,因为 close() 方法会清除图形并关闭窗口;我们使用 plt.show() 过程不会看到任何东西。
相关文章
Pandas DataFrame DataFrame.shift() 函数
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:133 分类:Python
-
DataFrame.shift() 函数是将 DataFrame 的索引按指定的周期数进行移位。
Python pandas.pivot_table() 函数
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:82 分类:Python
-
Python Pandas pivot_table()函数通过对数据进行汇总,避免了数据的重复。
Pandas read_csv()函数
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:254 分类:Python
-
Pandas read_csv()函数将指定的逗号分隔值(csv)文件读取到 DataFrame 中。
Pandas 多列合并
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:628 分类:Python
-
本教程介绍了如何在 Pandas 中使用 DataFrame.merge()方法合并两个 DataFrames。
Pandas loc vs iloc
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:837 分类:Python
-
本教程介绍了如何使用 Python 中的 loc 和 iloc 从 Pandas DataFrame 中过滤数据。
在 Python 中将 Pandas 系列的日期时间转换为字符串
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:894 分类:Python
-
了解如何在 Python 中将 Pandas 系列日期时间转换为字符串

