Python 中使用元组格式化字符串
使用格式化的字符串文字来执行带有元组的字符串格式化,例如 f'Tuple: {my_tuple}'。 格式化的字符串字面量让我们通过在字符串前面加上 f 前缀来在字符串中包含表达式和变量。
my_tuple = (2, 4, 6, 8)
# ✅ string formatting with a tuple
result = f'Tuple: {my_tuple}'
print(result) # 👉️ Tuple: (2, 4, 6, 8)
# ✅ string formatting and accessing specific tuple elements
result = f'first: {my_tuple[0]}, second: {my_tuple[1]}, third: {my_tuple[2]}, fourth: {my_tuple[3]}'
print(result) # 👉️ first: 2, second: 4, third: 6, fourth: 8
# ----------------------------------------
# ✅ using the str.format() method
result = 'first: {}, second: {}, third: {}, fourth {}'.format(*my_tuple)
print(result) # 👉️ first: 2, second: 4, third: 6, fourth 8
# ----------------------------------------
# ✅ join a tuple's elements with a separator
result = ','.join(str(item) for item in my_tuple)
print(result) # 👉️ '2,4,6,8'
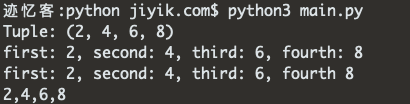
第一个示例使用格式化的字符串文字来执行带有元组的字符串格式化。
my_tuple = (2, 4, 6, 8)
result = f'Tuple: {my_tuple}'
print(result) # 👉️ Tuple: (2, 4, 6, 8)
格式化字符串文字
(f-strings)让我们通过在字符串前面加上f来在字符串中包含表达式。
my_tuple = (2, 4, 6, 8)
result = f'Tuple: {my_tuple}, length: {len(my_tuple)}'
print(result) # 👉️ Tuple: (2, 4, 6, 8), length: 4
确保将表达式包裹在花括号 - {expression} 中。
我们可以使用括号表示法来访问索引处的元组元素。
my_tuple = (2, 4, 6, 8)
result = f'first: {my_tuple[0]}, second: {my_tuple[1]}, third: {my_tuple[2]}, fourth: {my_tuple[3]}'
print(result) # 👉️ first: 2, second: 4, third: 6, fourth: 8
Python 索引是从零开始的,因此元组中的第一个元素的索引为
0,最后一个元素的索引为-1或len(my_tuple) - 1。
或者,我们可以使用 str.format() 方法。
my_tuple = (2, 4, 6, 8)
result = 'first: {}, second: {}, third: {}, fourth {}'.format(*my_tuple)
print(result) # 👉️ first: 2, second: 4, third: 6, fourth 8
str.format 方法执行字符串格式化操作。
调用该方法的字符串可以包含使用花括号 {} 指定的替换字段。
确保为
format()方法提供与字符串中的替换字段一样多的参数。
示例中的元组有 4 个元素,因此我们在字符串中指定了 4 个替换字段。
my_tuple = (2, 4, 6, 8)
result = 'first: {}, second: {}, third: {}, fourth {}'.format(*my_tuple)
print(result) # 👉️ first: 2, second: 4, third: 6, fourth 8
* 可迭代解包运算符使我们能够在函数调用、推导式和生成器表达式中解包可迭代对象。
可迭代解包运算符解包元组并将其元素作为多个逗号分隔的参数传递给
str.format()方法的调用。
如果我们需要使用分隔符将元组的元素连接成字符串,请使用 str.join() 方法。
my_tuple = (2, 4, 6, 8)
result = ','.join(str(item) for item in my_tuple)
print(result) # 👉️ '2,4,6,8'
str.join 方法将一个可迭代对象作为参数并返回一个字符串,该字符串是可迭代对象中字符串的串联。
如果我们的元组存储字符串,我们可以直接将元组传递给 str.join() 方法。
my_tuple = ('one', 'two', 'three')
result = ','.join(my_tuple)
print(result) # 👉️ 'one,two,three'
请注意,如果可迭代对象中有任何非字符串值,则str.join()方法会引发 TypeError。
调用 join() 方法的字符串用作元素之间的分隔符。
我们在示例中使用了逗号,但我们可以使用任何其他分隔符,例如 一个空字符串,用于连接不带分隔符的元组元素。
相关文章
Python pandas.pivot_table() 函数
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:82 分类:Python
-
Python Pandas pivot_table()函数通过对数据进行汇总,避免了数据的重复。
在 Python 中将 Pandas 系列的日期时间转换为字符串
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:894 分类:Python
-
了解如何在 Python 中将 Pandas 系列日期时间转换为字符串
在 Python Pandas 中使用 str.split 将字符串拆分为两个列表列
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:1124 分类:Python
-
本教程介绍如何使用 pandas str.split() 函数将字符串拆分为两个列表列。
在 Pandas 中将 Timedelta 转换为 Int
发布时间:2024/04/23 浏览次数:231 分类:Python
-
可以使用 Pandas 中的 dt 属性将 timedelta 转换为整数。
Python 中的 Pandas 插入方法
发布时间:2024/04/23 浏览次数:112 分类:Python
-
本教程介绍了如何在 Pandas DataFrame 中使用 insert 方法在 DataFrame 中插入一列。
使用 Python 将 Pandas DataFrame 保存为 HTML
发布时间:2024/04/21 浏览次数:106 分类:Python
-
本教程演示如何将 Pandas DataFrame 转换为 Python 中的 HTML 表格。
如何将 Python 字典转换为 Pandas DataFrame
发布时间:2024/04/20 浏览次数:73 分类:Python
-
本教程演示如何将 python 字典转换为 Pandas DataFrame,例如使用 Pandas DataFrame 构造函数或 from_dict 方法。
如何在 Pandas 中将 DataFrame 列转换为日期时间
发布时间:2024/04/20 浏览次数:101 分类:Python
-
本文介绍如何将 Pandas DataFrame 列转换为 Python 日期时间。

