Executing multiple commands in Docker-Compose
Docker makes it easier for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about dependencies by packaging them in standardized units called containers. Docker-compose is an advanced, must-have tool for managing multi-container applications.
You can use docker-compose to define instructions to manage services that depend on multiple Docker containers.
In addition to being able to manage multiple containers, docker-compose provides other benefits such as isolated environments for application services and preservation of volume data when creating containers.
Executing multiple commands in Docker-Compose
Docker-compose runs on the Docker Engine and is installed with Docker on Mac and Windows machines. The following command allows you to verify that docker-compose is set up correctly on your machine.
$ docker-compose version
Docker Compose version v2.2.3
In the following example, we will discuss how to set up a Django, PostgreSQL application using docker-compose. We will discuss how to execute multiple commands in docker-compose.
First, we will create a simple Dockerfile with simple entries as shown below. This file outlines the commands that will be executed to create our Docker image.
FROM python:3
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
WORKDIR /tonyloi
COPY requirements.txt /code/
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . /tonyloi/
The Dockerfile defines Python 3 as the base image; however, we also define a requirements.txt file to describe other requirements needed for the project to run.
Django>=3.0,<4.0
psycopg2>=2.8
Now that you have these two files ready, you can create the docker-compose.yml file in the root directory of this project. This file describes the application services we intend to build: the database and the web server.
In addition to this, we will also define the Docker images that these services use and any other Docker volumes you may wish to mount. Finally, we also need to specify the ports that the services will expose.
Since this is a Django application, we must also specify the command that will allow us to run migrations and start the development server. There are several ways to do this, using either sh or bash.
In this case, we will use sh since it is available on Unix-based systems.
docker-compose.yml:
version: "3.9"
services:
DB:
image: Postgres
volumes:
- ./data/db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=postgres
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
web:
build: .
command: >
sh -c "
python manage.py migrate &&
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8080"
volumes:
- .:/tonyloi
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- POSTGRES_NAME=postgres
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password
depends_on:
- DB
We will run the following docker-compose runcommand to create this Django project. Before executing this command, you must make sure that you are in the root directory.
If not, use the cd command to navigate to the root directory.
~/django_app$ sudo docker-compose run web Django-admin startproject new_app .
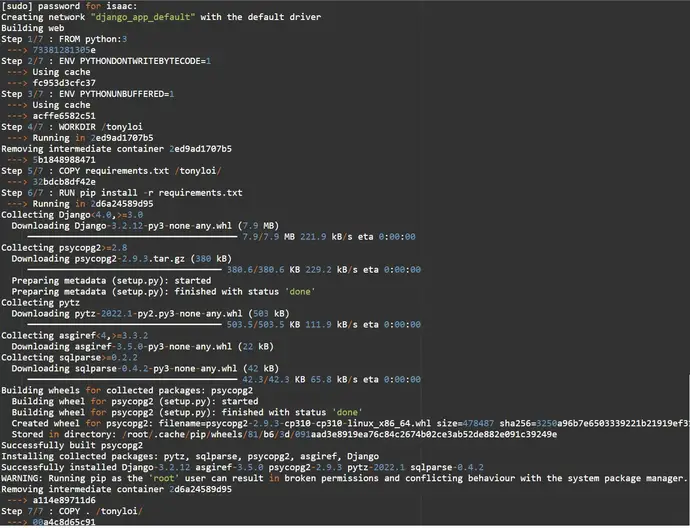
Output:
Successfully built 00a4c8d65c91
Successfully tagged django_app_web:latest
WARNING: Image for service web was built because it did not already exist. To rebuild this image you must use `docker-compose build` or `docker-compose up --build`.
Creating django_app_db_1 ... done
Creating django_app_web_run ... done
This command uses docker-compose and the Docker file to create a Django project. In this example, we name the project new_app.
You can now navigate to the project and list the project files.
isaac@DESKTOP-HV44HT6:~/django_app$ cd new_app
isaac@DESKTOP-HV44HT6:~/django_app/new_app$ ls
__init__.py asgi.py settings.py urls.py wsgi.py
isaac@DESKTOP-HV44HT6:~/django_app/new_app$
This article focuses on how to use sh to execute multiple commands in a docker-compose file. Alternatively, you can also use bash -cas shown below.
command: bash -c "
python manage.py migrate &&
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8080
"
We can finish creating the rest of our Django application by configuring our database settings in the settings.py file.
Django uses SQLite by default when developing; therefore, since we are using PostgreSQL, we need to make the necessary configuration below. Be sure to replace the database and username with your own.
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql',
'NAME': os.environ.get('postgres'),
'USER': os.environ.get('postgres'),
'PASSWORD': os.environ.get('enter_your database'),
'HOST': 'db',
'PORT': 5432,
}
}
Finally, to start, the application executes the command in the project's main directory sudo docker-compose up. It starts the development server at http://0.0.0.0:8080/, as we specified in the docker-compose file.
~/django_app$ sudo docker-compose up

For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Get the IP address of the Docker container from the host using docker inspect
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:103 Category:Docker
-
Docker containers are not just for isolation—they are often used to manage processes that still need to communicate directly with each other. However, to communicate, you usually need to know the IP address of each container, which you ca
Solution to incorrect access log time when deploying Nginx in Docker
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:165 Category:Docker
-
In the process of operating the website, I never took the logs too seriously. Although logging was turned on, I never analyzed the logs carefully. Today, when I looked at the logs on a whim, I found that the recorded time was 8 hours less t
Docker deploys nginx php application
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:131 Category:Docker
-
I'm learning docker recently. I'm learning by building an nginx+php development environment example. Here I record the build process. First, give a docker-compose.yml deployment configuration file version: '3' services: nginx: container_nam
How to use Docker to image a Node.js web application
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:107 Category:Docker
-
Docker is a containerization platform that simplifies the packaging and execution of applications. Containers run as independent processes with their own file systems, but share the kernel of their host machine. Docker has attracted much at
Start a Bash terminal in a new Docker container
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:97 Category:Docker
-
Docker containers are a standard unit for packaging all the dependencies of an application, allowing us to easily run them in any environment. Containers have become very popular recently, and most developers now rely heavily on containers
Passing environment variables to containers in Docker
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:125 Category:Docker
-
This article will introduce how to pass environment variables to containers in Docker. Passing environment variables to containers in Docker using the -e and tags -env We will first see how to create environment variables and pass them to t
Install Docker using Homebrew
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:202 Category:Docker
-
There is no doubt that Docker containers have revolutionized the way we develop and deploy applications. They provide developers with the ability to package applications and dependencies in an isolated environment. Recently, we've seen wide
Enforce clean build of images in Docker
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:88 Category:Docker
-
This article discusses and demonstrates how to enforce clean builds of images in Docker. Building images in Docker We will use a simple Flask application to demonstrate this concept. my-app Create a app.py simple application named in the ho
Running a Docker instance from a Dockerfile
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:140 Category:Docker
-
Docker containers have undoubtedly become the standard unit for managing software and dependencies in different environments. When using real applications, you must create a docker file before building the container image of the application

