Get the IP address of the Docker container from the host using docker inspect
Docker containers are not just for isolation—they are often used to manage processes that still need to communicate directly with each other. However, to communicate, you usually need to know the IP address of each container, which you can find out with a few commands.

Consider using a user-defined bridge
Docker networking is a bit complicated. Containers started by default will be placed in the default "bridge network" and will be allowed to communicate directly with other containers, provided you have their private IP addresses. This option can be turned off for true isolation, but it is not by default.
You can also use this address to communicate with the host operating system if you don't want to bind a port. This is the primary use case for accessing a container directly by its IP address, but you should probably still just bind a single port (which can be firewalled off from the internet).
However, IP addresses are temporary and can easily break when containers are stopped and started. For communication between containers, Docker provides a solution through user-defined bridge networks, which you probably want to use if you have multiple containers communicating with each other.
Containers added to non-default networks will be able to access each other through their aliases, which will automatically resolve to private IPs. You can create new networks, run containers in these networks, and connect existing containers to networks. You can then access other containers using the aliases as hostnames; for example, the NGINX container here can mongodb://mongohost:27017access the MongoDB instance through the connection string.
$ docker network create example
$ docker run --net example --name nginx -d nginx
$ docker network connect example --alias mongohost mongodb
While using a bridge has many benefits, it is recommended to use the traditional --linkoption, which works well with the default network. The main issue is that containers in a user-defined network will expose ports to each other, whether they are published or not, but you can set up multiple networks so this is usually not a problem.
Another downside is that, since user-defined networks provide better isolation, they also do not allow you to access containers across networks using their private IP addresses. All containers in the default network can communicate with each other, but once it is removed and placed in a user-defined network, this functionality is disabled. However, we can also start containers in only the default and user-defined networks, so this is not a problem if you choose to make your containers visible to others.
Get the IP address from Docker
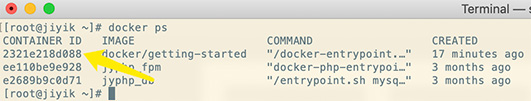
If you just want the IP address, getting it from the host operating system is pretty straightforward. First, you need to find the ID or name of the container you want information about. You can get the container using the following command:
$ docker ps
Then, run it docker inspect, and it will return a giant JSON file with all the information about the container. We are only interested in the IP address, though, so we can -fpass it a formatting option using the option to narrow it down to just the IP address.
docker inspect -f '{{range.NetworkSettings.Networks}}{{.IPAddress}}{{end}}' name_or_id

This command works well, but it only returns information about the container with the ID you specify. If you want a more specific solution, you can use docker network inspectprint information about all containers in a given network, optionally formatted as a JSON lookup table:
docker network inspect bridge -f '{{json .Containers}}'
The output is as follows
{
"2321e218d0880e8520de254b4bd2773ccf67c5d7e00fe1fc5a53a8bd1113a48d": {
"Name": "cranky_snyder",
"EndpointID": "2e8210889328695ba2a07262993ec8550ea2dd7e592b008ede989e6cac943372",
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"IPv4Address": "172.17.0.2/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
}
}
Get the network configuration of the container
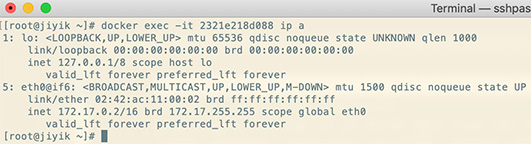
The Docker container is actually just an isolation mechanism. We can enter the container just like logging into a normal host and run ifconfigregular Linux commands such as and obtain the IP address in this way.
To do this, we need to docker psget the container name or ID using , and then run exec -it. In this case, print out all IP information:
docker exec -it 2321e218d088 ip a
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Solution to incorrect access log time when deploying Nginx in Docker
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:165 Category:Docker
-
In the process of operating the website, I never took the logs too seriously. Although logging was turned on, I never analyzed the logs carefully. Today, when I looked at the logs on a whim, I found that the recorded time was 8 hours less t
Docker deploys nginx php application
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:131 Category:Docker
-
I'm learning docker recently. I'm learning by building an nginx+php development environment example. Here I record the build process. First, give a docker-compose.yml deployment configuration file version: '3' services: nginx: container_nam
How to use Docker to image a Node.js web application
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:107 Category:Docker
-
Docker is a containerization platform that simplifies the packaging and execution of applications. Containers run as independent processes with their own file systems, but share the kernel of their host machine. Docker has attracted much at
Start a Bash terminal in a new Docker container
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:97 Category:Docker
-
Docker containers are a standard unit for packaging all the dependencies of an application, allowing us to easily run them in any environment. Containers have become very popular recently, and most developers now rely heavily on containers
Passing environment variables to containers in Docker
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:125 Category:Docker
-
This article will introduce how to pass environment variables to containers in Docker. Passing environment variables to containers in Docker using the -e and tags -env We will first see how to create environment variables and pass them to t
Install Docker using Homebrew
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:202 Category:Docker
-
There is no doubt that Docker containers have revolutionized the way we develop and deploy applications. They provide developers with the ability to package applications and dependencies in an isolated environment. Recently, we've seen wide
Enforce clean build of images in Docker
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:88 Category:Docker
-
This article discusses and demonstrates how to enforce clean builds of images in Docker. Building images in Docker We will use a simple Flask application to demonstrate this concept. my-app Create a app.py simple application named in the ho
Running a Docker instance from a Dockerfile
Publish Date:2025/03/26 Views:140 Category:Docker
-
Docker containers have undoubtedly become the standard unit for managing software and dependencies in different environments. When using real applications, you must create a docker file before building the container image of the application
Copy files from host to Docker container
Publish Date:2025/03/25 Views:127 Category:Docker
-
This article will discuss and demonstrate methods we can use to transfer files from the host to a running container in Docker. docker cp Copy the file from the host to the Docker container using docker cp The command is one of the simplest

