Managing version numbers in Git
This article provides an overview of how to manage version numbers in Git. We will use semantic versioning because it is the most widely used version control scheme.
Managing version numbers in Git
Before we get into management, let’s define some terms.
Semantic Versioning
Semantic versioning is just a numbering scheme. We use it as an industry standard software development metric to show how much a release has changed since the last release.
It is a clear and concise way to indicate the level of change and is widely used by developers.

The semantic version number consists of three parts:
- Main Parts
- Secondary part
- Patch number
We won't go into depth defining each part and its function, but here's a quick diagram.
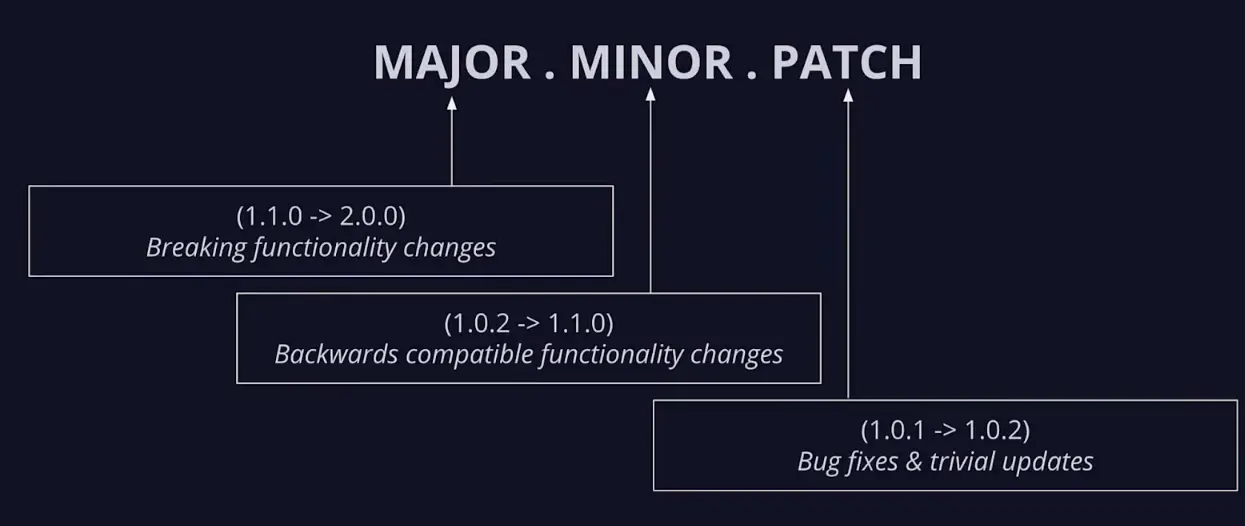
Semantic versioning requires us to double-check your version numbers before releasing your code. This makes the pattern a good fit for grouping Git tags.
Git tags
We use Git tags to mark a meaningful commit. Git has two kinds of tags.
- Lightweight Tags
- Annotated Tags
A lightweight tag is a simple named pointer. Here is an example.
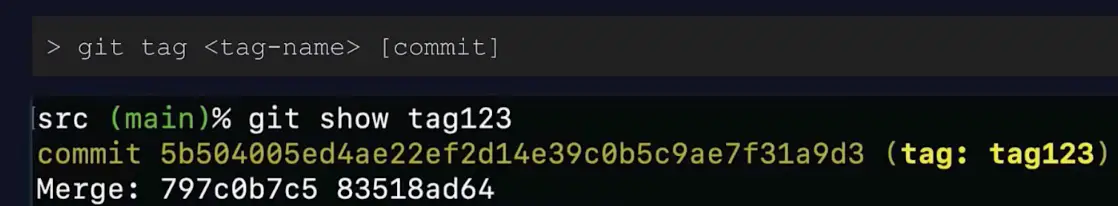
Annotated tags, on the other hand, contain more detailed information about a commit. We can mark it as an annotated tag using the commit command with the -a flag and provide a description using the -m flag.git tag
Here is an example.
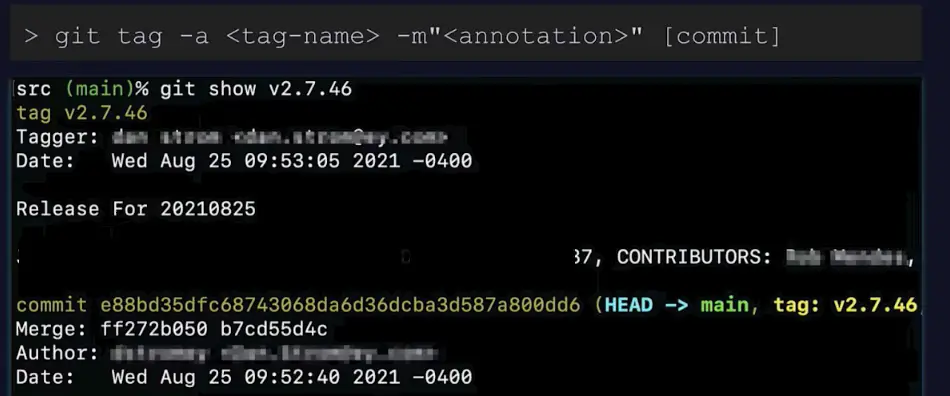
Annotated Git Tags + Semantic Versioning
Using annotated Git tags and semantic versioning allows us to label commits in our repository with version numbers. Some Git products with interfaces support semantic versioning of Git tags.
Here is an example on a Mac.
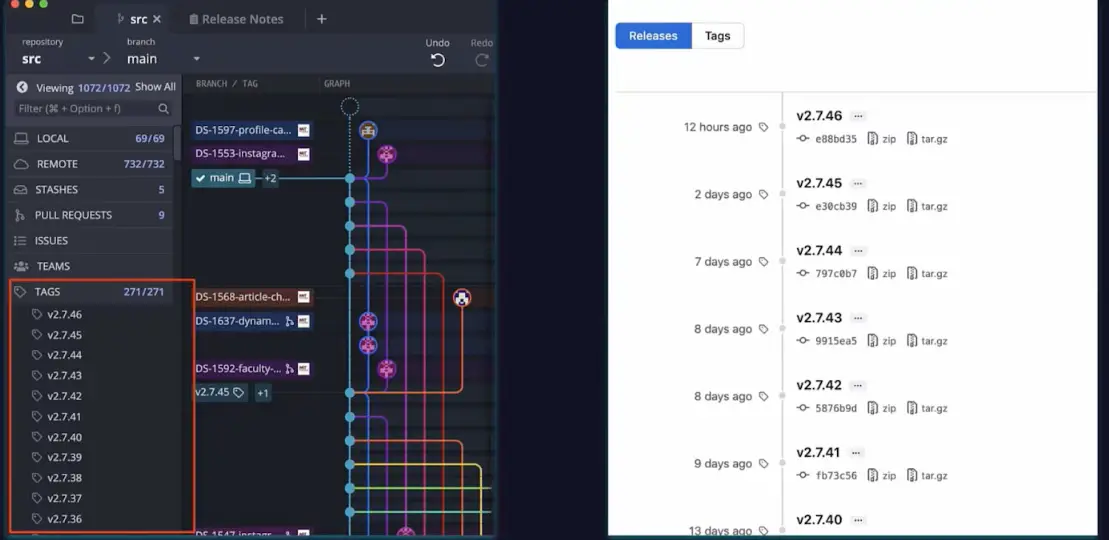
As shown below, we can run the git tag command to tag a commit using the semantic versioning scheme.
$ git tag - "v1.2.0-beta" -m "version v1.2.0-beta"
The command above adds the v1.2.0-beta tag to our repository. To view the details of the tag, we can run:
$ git show v1.2.0-beta
In short, semantic versioning combined with annotated Git tags provides a perfect way to indicate the level of changes to a codebase. We have already covered how to use semantic versioning of your repository with Git tags.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Article URL:https://www.jiyik.com/en/xwzj/opersys_10243.html
Related Articles
Git diff shows diff details of uncommitted changes
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:105 Category:Git
-
This article outlines how we can get diff details of uncommitted work in Git. We use the git diff command to show the differences between various Git references, such as commits, the index, and the working tree. We can use this command to d
Staging area in Git
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:151 Category:Git
-
In this article, we will learn about the staging area in Git . Git is a version control system that maintains a history of changes made to a project directory. Git uses commits to track changes. Git has three internal management systems, on
Add all files in a folder to commit in Git
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:158 Category:Git
-
This article will discuss the necessary steps to add all of your files into one folder for submission. If you have a folder with a dozen files, adding the files one by one can be tedious. Fortunately, Git allows us to add all the contents o
Meaning of Fetch_Head in Git
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:64 Category:Git
-
This article defines Fetch_HEAD in Git . This reference is an integral part of the git pull command and is important when merging changes from a remote repository into a local repository or branch. If you're not sure what Fetch_Head means,
Get all branches in Git
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:62 Category:Git
-
This article discusses how to fetch all branches from a remote repository. The git fetch command is a useful utility when you want to download changes from a remote repository without having to update your local branches. Sometimes, you may
Clone a Git repository with a specific revision
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:82 Category:Git
-
This article discussed various methods that we can use to clone a Git repository with a specific revision or changeset. This comes in handy when you have a repository with large files and you only need a specific version of the code. Instea
Squash commits pushed in Git
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:86 Category:Git
-
This article outlines the process of squashing commits that we have pushed to a remote repository. We squash the commits into one to reduce clutter in the repository. To squash the commits, we run git rebase in interactive mode . Squash com
Git squash all commits
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:65 Category:Git
-
In every developer’s life, the word squash is often used while working with the Git distributed control system . This feature in Git is a handy option that developers often use to achieve a neat workflow in their development team. In this
Close the Git commit editor on Windows
Publish Date:2025/03/31 Views:62 Category:Git
-
In this article, we will discuss how to exit the Git commit editor. This can be a little tricky, especially if you are new to Git bash . Let's see how to exit the editor on Windows. Close the Git commit editor on Windows We will look at a t

