Handling onScroll Events in React (with Examples)
Handling onScroll events on div elements in React
Handling onScroll event in React:
-
Set the property on the element
onScrollto listen for scroll events. - Provides event handling functions.
-
Access
event.currentTarget.scrollTopthe property to get the number of pixels to scroll vertically.
import {useState} from 'react';
export default function App() {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const handleScroll = event => {
setScrollTop(event.currentTarget.scrollTop);
};
return (
<div>
<h2>Scroll Top: {scrollTop}</h2>
<div
style={{
border: '3px solid black',
width: '400px',
height: '100px',
overflow: 'scroll',
}}
onScroll={handleScroll}
>
{[...Array(20)].map((_, index) => (
<p key={index}>Content {index}</p>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
}
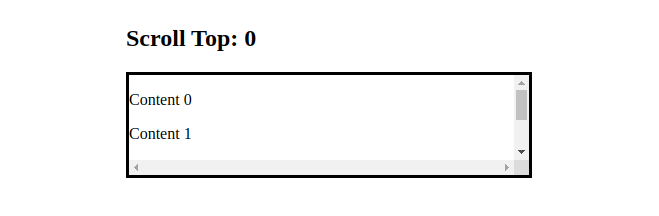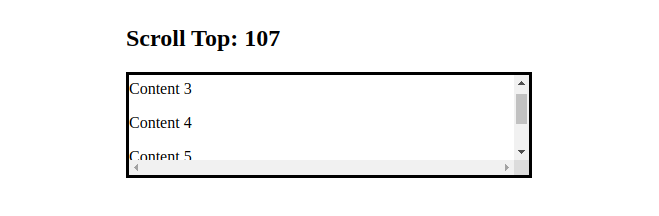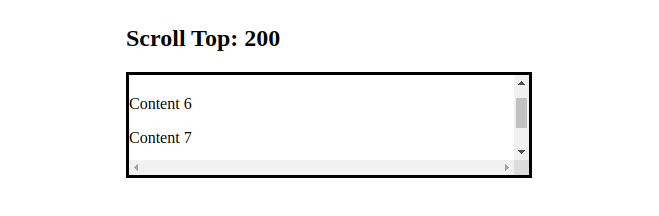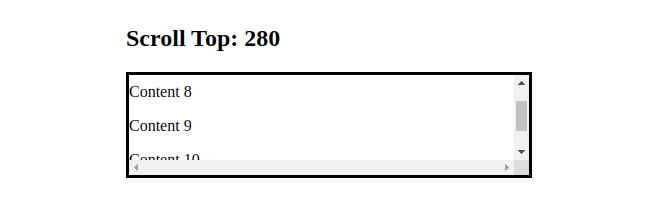
We set onScrollthe property on the div element, so each time the user scrolls the div's horizontal or vertical axis, handleScrollthe function will be called.
请注意, we use the event object'scurrentTargetproperty to access the element.
const handleScroll = event => {
setScrollTop(event.currentTarget.scrollTop);
};
The event's
currentTargetproperty gives us access to the element to which the event listener is attached.
On the other hand, the target property of the event gives us a reference to the element (possibly a descendant) that triggered the event.
We use Element.scrollTopthe property to get the number of pixels to scroll the element's content vertically.
The final step is to update the state variables using useStatethe hook.
setScrollTop(event.currentTarget.scrollTop);
setScrollTopThe function is responsible for updating the state variable every time the div's vertical axis is scrolled scrollTop.
We can use the method to handle events addEventListeneron the window object .onScroll
Handling onScroll event on window object in React
To handle the onScroll event on the window object:
-
Adds a scroll event listener to
useEffectthe window object in the hook. -
Use
window.scrollYthe property to get the number of pixels to scroll the document vertically.
import {useEffect, useState} from 'react';
const App = () => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = event => {
setScrollTop(window.scrollY);
};
window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
};
}, []);
return (
<div>
<div
style={{
position: 'fixed',
padding: '10px 0',
top: '0',
backgroundColor: 'white',
borderBottom: '3px solid black',
width: '100%',
}}
>
<h2>Scroll Top: {scrollTop}</h2>
</div>
<div style={{marginTop: '10rem'}}>
{[...Array(100)].map((_, index) => (
<p key={index}>Content {index}</p>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
addEventListenerThe method takes the following 2 parameters:
- Type Enter the event type to be monitored
- The function called when the listener event is triggered
Scroll events are fired when the document view is scrolled.
We pass an empty dependenciesarray to the useEffect hook because we only want to register the scroll event listener once - when the component mounts.
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = event => {
setScrollTop(window.scrollY);
};
window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
};
}, []);
We use window.scrollYthe property to update the scrollTop state variable.
The window object's window.scrollYscroll property returns the number of pixels the document is currently scrolled vertically.
If we set the attribute on the element onScroll, we will use Element.scrollTopthe attribute instead, as shown in the previous subheading.
The function we return from the useEffect hook is called when the component unmounts.
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
};
We use removeEventListenerthe method to remove the event listener we registered previously.
removeEventListenerThe method takes the following 2 parameters:
- typeType the event type for which you want to remove the event listener
- listener The event listener function of the event handler to be removed from the event target
The cleanup step is important because we want to make sure that we don't have any memory leaks in our application.
scrollTopProperty returns the number of pixels to scroll the element's content vertically.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
How to avoid cross-origin (CORS) issues in React/Next.js
Publish Date:2025/03/17 Views:170 Category:NETWORK
-
In this article, we will introduce how to avoid cross-origin (CORS) issues in React/Next.js. Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a protocol that defines how web requests should be handled when crossing different URLs.
React Tutorial - Transferring Props
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:188 Category:React
-
React transfers Props. Props are generated when components are encapsulated. Components expose some properties (Props) to the outside world to complete some functions.
React Tutorial: Props Anti-Pattern
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:187 Category:React
-
React's Props anti-pattern, using Props to generate state in getInitialState is an anti-pattern - Anti-Pattern.
React Tutorial - Props Validation
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:102 Category:React
-
Props validation is a very useful way to use components correctly. It can avoid many bugs and problems as your application becomes more and more complex. In addition, it can make your program more readable.
React tutorial: Types of Props for child components
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:172 Category:React
-
Usually, the child components of a React component are a group, that is, the child components are an array. Introduction to Type of the Children Props.
How to solve the error Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined in
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:153 Category:React
-
In the process of React development, we often encounter some errors. Here we look at an error reported in App.js. The error is as follows: App.js:69 Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'setState') at onInput
Why do you need to bind event handlers in React Class Components?
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:60 Category:React
-
When using React, we must have come across control components and event handlers. We need to use `.bind()` in the constructor of the custom component to bind these methods to the component instance. As shown in the following code:
Solution to the error "does not contain a default export" in React
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:191 Category:React
-
When we try to use `default import` to import from a module that does not have a `default export`, we get a "does not contain a default export" error. To fix the error, make sure the module has named exports and wrap the import in curly braces, e.g.
Error in React: Attempted import error 'X' is not exported from Solution
Publish Date:2025/03/16 Views:78 Category:React
-
In React, the error “Attempted import error 'X' is not exported from” in React.js occurs when we try to import a named import that does not exist in the specified file. To fix the error, make sure the module has named exports and you have not obfu

