Linux Sed Tutorial: 6 Examples of Sed Branching Operations
Like any other programming language, sed also provides special branching commands to control the flow of the program.
In this article, let's review the following two types of Sed branches.
- Sed unconditional branch
- Sed conditional branching
Sed unconditional branch syntax:
$ sed ':label command(s) b label'
- :label - Label specification.
- commands – any sed commands
- label – any name for the label
- blabel - jump to label without checking any conditions. If label is not specified, jump to the end of the script.
Sed conditional branch syntax:
$ sed ':label command(s) t label'
- :label - Label specification.
- commands – any sed commands
- label – any name for the label
- tlabel - Jump to label only if the last substitution command modified the pattern space. If label is not specified, jump to the end of the script.
Creating a sample test file
Let us first create the jiyik_sed.txt file which will be used in the examples mentioned below .
jiyik_sed.txtLinux Administration Scripting Tips and Tricks Windows Administration Database Administration of Oracle Administration of Mysql Security Network Online\ Security Productivity Google Search\ Tips "Web Based Time Tracking, Web Based Todo list and Reduce Key Stores etc"
Check the file contents as follows

Sed Example of Unconditional Branching
Sed Example 1. Replace the first occurrence of a pattern in the entire file
In the file jiyik_sed.txt, replace the first occurrence of “ Administration ” with “ Supervision ”.
$ sed '/Administration/{
s/Administration/Supervision/
:loop
n
b loop
}' jiyik_sed.txt
Let’s look at the results

- In the above sed command, it simply reads and prints the pattern space line by line until it matches Administration .
- Once Administration is matched , replace Administration with Supervision (only appears once, note there is no "g" flag replacement).
-
Once the first match is replaced, just read the remaining file contents and print them.
-
nis a sed command that prints the pattern space and overwrites it with the next line. -
Use
loopas label.nPrint the current line and overwrite the pattern space with the next line.bThe loop jumps to again:loop. So this loop prints the rest of jiyik_sed.txt .
-
“”sed Example 2. Delete the data between
the double quotes of the pattern in the entire file
In our example file, “”there are three lines between.
$ sed -e ':loop
$!{
N
/\n$/!b loop
}
s/"[^"]*"//g' jiyik_sed.txt
See the following running results

-
The above command keep appends all the lines of the file until the end of the file.
- $! – if it is not end of file.
-
N - Append the next line, with the pattern space
\nseparated by - /\n$/!b loop - If this is not the last line of the file, jump to the loop again.
-
Now all the lines will be available in the pattern space separated by newline characters. Replace
“”all the occurrences of data in between with nothing.
Sed Example 3. Remove HTML tags from a file
For example, I have a file with the following html content
index.html<html><body> <table border=2><tr><td valign=top align=right>1.</td> <td>Line 1 Column 2</ td> </table> </body></html>
The following sed command removes all html tags from a given file
$ sed '/</{
:loop
s/<[^<]*>//g
/</{
N
b loop
}
}' index.html
See the following running results
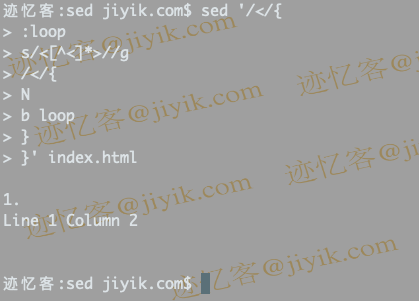
- Each time a line containing '<' is found, all HTML tags in that line are first deleted.
- If the pattern space now contains "<", this means a multi-line tag. Now repeat the following loop:
- Join next line
- Remove all HTML tags until there is no single "<"
- When "<" is not present in the pattern space, we print it out and start a new loop.
Sed Example of Conditional Branching
Sed Example 4. If a line ends with a backslash, append the next line to it
Our sample file has two lines ending with a backslash, and now we have to append the next line to it.
$ sed '
:loop
/\\$/N
s/\\\n */ /
t loop' jiyik_sed.txt
See the following running results

-
Checks if the line
(/\\$/)ends with a backslash , and if so, reads the next line and appends it to the pattern space,\\replacing the at the end of the line and the number of spaces that follow with a single space. - If the replacement is successful, repeat the above steps. The branch will only be executed if the replacement is successful.
- Conditional branches are mainly used in recursive patterns.
Sed Example 5. comify a numeric string
$ sed '
:loop
s/\(.*[0-9]\)\([0-9]\{3\}\)/\1,\2/
t loop'
12342342342343434
12,342,342,342,343,434
See the results below

- Divide the numbers into two groups.
- The first group is all the numbers up to the last three digits. The last three digits are captured in the second group.
- The two matching groups are then separated by a comma. The same rule is then applied to the line again and again until all the numbers have been grouped into groups of three.
-
For example, in the first iteration it will be
12342342342343,434 -
In the next iteration
12342342342,343,434, until there are fewer than three digits.
Sed Example 6. Formatting: Replace each leading space in a line with "+"
$ sed '
s/^ */&\n/
:loop
s/^\n//;s/ \n/\n+/
t loop' jiyik_sed.txt
See the following running results

- Separate all leading spaces and other characters of the line with a newline character.
-
Now replace spaces and newlines with
+and . So, from right to left, spaces will be replaced with+and newlines will be shifted one character to the left. -
Finally at the beginning of the line
\nwill be there, so delete that new line.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Restart PostgreSQL in Ubuntu 18.04
Publish Date:2025/04/09 Views:72 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This short article shows how to restart PostgreSQL in Ubuntu. Restart PostgreSQL Server in Ubuntu You can restart Postgres server in Ubuntu using the following command. Order: sudo service postgres restart Sometimes the above command does n
Issues to note when installing Apache on Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:78 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
As the most commonly used web server, Apache can be used in most computer operating systems. As a free and open source Unix-like operating system, Linux and Apache are a golden pair. This article will introduce the installation and use of A
How to decompress x.tar.xz format files under Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:186 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
A lot of software found today is in the tar.xz format, which is a lossless data compression file format that uses the LZMA compression algorithm. Like gzip and bzip2, it supports multiple file compression, but the convention is not to compr
Summary of vim common commands
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:115 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
In Linux, the best editor should be vim. However, the complex commands behind vim's powerful functions also make us daunted. Of course, these commands do not need to be memorized by rote. As long as you practice using vim more, you can reme
Detailed explanation of command return value $? in Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:58 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
? is a special variable. This variable represents the return value of the previous command. That is to say, when we run certain commands, these commands will return a code after running. Generally, if the command is successfully run, the re
Common judgment formulas for Linux script shell
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:159 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
In shell script programming, predicates are often used. There are two ways to use predicates, one is to use test, and the other is to use []. Let's take a look at how to use these two methods through two simple examples. Example 1 # test –
Shell script programming practice - specify a directory to delete files
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:98 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Usually, in Linux system we need to frequently delete some temporary files or junk files. If we delete them one by one manually, it will be quite troublesome. I have also been learning shell script programming recently, so I tried to write
Use of Linux command at - set time to execute command only once
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:158 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
This article mainly involves a knowledge point, which is the atd service. Similar to this service is the crond service. The functions of these two services can be similar to the two functional functions of javascript. Those who have learned
Use of Linux command crontab - loop execution of set commands
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:170 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Compared with at , which executes a command only once, crontab, which we are going to talk about in this article, executes the set commands in a loop. Similarly, the use of crontab requires the support of the crond service. The service is s

