MySQL CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() Function Detailed Introduction (with Examples)
This article explains how to use MySQL functions with examples CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(). By using it, we can convert or display the current date and time.
The output format is "YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS" or "YYYYMMDDHHMMSS", depending on the context in which the function is called, whether it is a number or a string. The functions NOW() and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() are equivalent to CURRENT_TIMESTAMP.
Note that the examples shown here will give results based on the current date.
MySQL CURRENT_TIMESTAMP()
This function confirms that it can start from MySQL version (such as 3.23, 4.0, 4.4, 5.6, 5.7, etc.).
The form is as follows
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP();
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(FSP);
The second form of the FSP parameter indicates the fractional seconds precision of the resulting value. If you want a more precise time value, use the second format.
Now let's see some examples of using MySQL CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() function.
String context
In this example, we print the current timestamp value in a string context.
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP();
The above MySQL statement will generate a date in standard string format. The result is as follows:
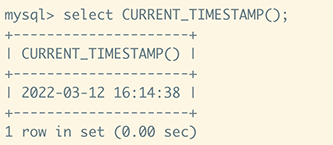
Numerical context
Let's look at an example of using the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() method in a numeric context.
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() + 0;
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() + 1;
The above example results are as follows:
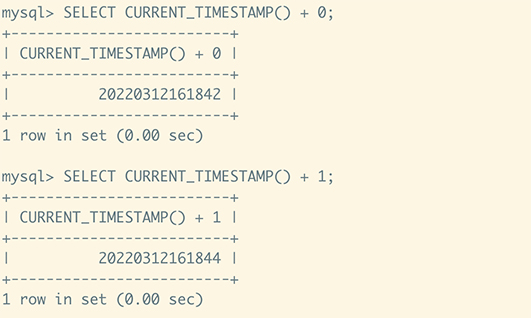
Fractional seconds precision
In this example, we pass the FSP value to set the fractional seconds precision in the result.
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(5);
The result is shown below
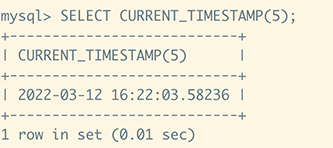
Summarize
Hopefully, we should now feel comfortable using the MySQL CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() function. However, we can take a look at some more examples and exercises.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Two ways to install mysql-5.5.47 on Linux system and manage mysql
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:140 Category:MySQL
-
We know that there are generally two ways to install software on the Linux system. One is to use rpm or yum to install, which is convenient and fast; the other is to use the compiled source package. Although this method is more troublesome
Mysql master-slave replication simple configuration
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:120 Category:MySQL
-
I'm learning about MySQL master-slave replication recently and want to apply it to a project at work. Since I'm new to it, I don't understand it very well, so I can only share how to make a simple configuration. At the beginning, we configu
Implementation details of MySQL master-slave replication (I) Exploration of the m
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:56 Category:MySQL
-
This article mainly discusses the implementation mechanism of master-slave replication, which may not be directly helpful for our actual application, but understanding its principle can achieve twice the result with half the effort for futu
Implementation details of MySQL master-slave replication (II) Exploration from th
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:74 Category:MySQL
-
Previously we explored the master server in master-slave replication. Now let's look at how the slave server works in the entire system. In the article Master Server Exploration, we mentioned that three threads are needed in a master-slave
Mysql master-slave replication - what to do if the slave server stops
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:97 Category:MySQL
-
You may find this topic a little ridiculous. What can we do if the server stops? Of course, we should restart the service. Restarting the service is no problem. The problem is that a lot of data has been written to the master database durin
MySQL stored procedure details
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:163 Category:MySQL
-
A stored procedure can be thought of as encapsulating a SQL statement that we need to process specially into a function. When needed, we only need to call this function to achieve the desired operation. This process can be called a stored p
How many of these MySQL statement tags have you used?
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:122 Category:MySQL
-
In the article "A Peek into MySQL Stored Procedure Details" , we briefly introduced the use of stored procedures. The syntax for creating stored procedures includes BEGIN...END. In addition to BEGIN...END, the following statement tags can b
How to back up a Kubernetes MySQL Operator cluster
Publish Date:2025/04/26 Views:79 Category:MySQL
-
Oracle's MySQL Operator for Kubernetes is a convenient way to automatically configure a MySQL database within a cluster. One of the key features of the Operator is the integrated automatic backup support for increased resiliency. The backup
How to select from multiple tables in MySQL
Publish Date:2025/04/25 Views:58 Category:MySQL
-
This article explains how to use MySQL to query from multiple tables in one script SELECT . Let's demonstrate a situation: SELECT name , price, details, type , FROM food, food_order WHERE breakfast.id = 'breakfast_id' Now, let's imagine FRO

