The difference between Fork and Branch on GitHub
This article discusses the difference between Form and Branch on GitHub. In the context of coding, the current era relies more on collaboration.
GitHub is one of the most commonly used collaboration tools. Forking and branching on GitHub are some of the most useful utilities when collaborating on a project.
However, the two have different use cases and meanings, as explained below.
The difference between forks and branches on GitHub
Forking on GitHub involves creating a copy of a public repository in your personal account. This concept encourages divergent evolution of the code base.
Divergent Evolution is ideal for those who wish to conduct extensive experiments on a single topic.
On the other hand, branching involves creating a branch from the origin. It encourages convergent evolution of the code base.
Most businesses prefer branching because of the positive impact it has on the productivity of the team.
Divergent and convergent evolution
You may have noticed that in the open source world, a code base may be split into two projects at the same time. Take the Linux code base as an example.
We now have several forks, such as Linux RedHat, but they all have a common ancestor. This is an example of divergent evolution of a code base.
It’s important to note that these iterations are not temporary development paths that will never merge into one another.
On the other hand, branches are temporary development paths. When code is merged into the master branch, the branch is short-lived.
That's why they encourage convergent evolution of code bases.
Fork creates a new repository
GitHub makes it easy to create a branch with the click of a button. This action creates a copy of the repository at the time of forking.
When is the best time to fork?
This is when you want to create a standalone project without intending to regroup it with its parent project.
You may come across a project on GitHub that would be a great starting point for your project. At moments like these, forking would be most ideal.
Fork on GitHub
Branches act as build zones in your codebase. We use branches to work on features temporarily with the goal of merging with origin.
To create a branch on GitHub , go to View All Branches and click New Branch.
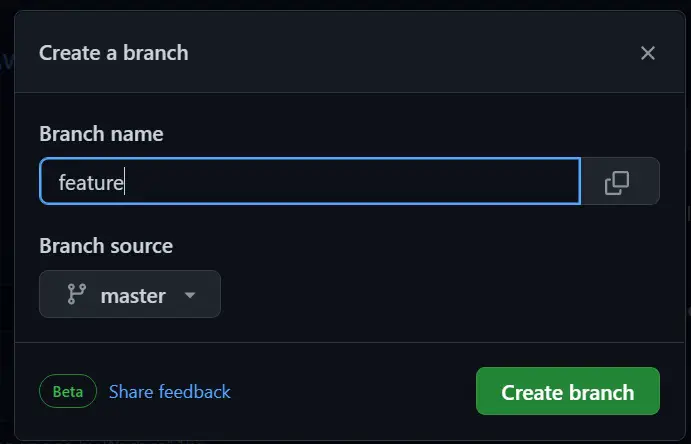
To create a new branch locally, we use git checkoutthe command as shown below.
$ git checkout -b <新分支>
How much does forking and branching cost?
Merging branches is easier and faster because Git only compares the files that have changed. Forking, on the other hand, can be considered more expensive.
When merging a branch with its original parent, Git has to compare the two repositories.
请记住, forking creates a copy of the entire parent repository.
The file size of the new branch will vary depending on the parent branch. Forking will take up more space on the remote server.
Businesses are encouraged to establish branches as this improves visibility and reduces operational risks.
Here are the reasons:
Let's say we have a team of ten people working on different features in a project. When each developer creates a branch, we will have ten different and independent repositories.
This will make it difficult to see what everyone is working on unless you have all 10 repositories in one place.
This is not a true collaborative environment because code changes exist in ten different repositories.
If developers choose ten different branches instead of forking, it will be more of a collaborative space because all commits are in one repository. This argument caters to the issue of visibility.
When we talk about operational risk, let's say a developer creates ten forks and one or two of them are unavailable for some reason. This introduces a knowledge management risk where the other developers won't know where the other developers have arrived.
This isn't always the case, but it's still possible to avoid this risk by adopting a branch-centric workflow.
A branch-centric workflow is best suited for business environments, while forking is best suited for public collaboration and experimentation. If you are both working towards a common goal, choose a branch-centric workflow.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Git installation and establishment of local warehouse service
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:89 Category:Git
-
Git is a distributed version control system: the client does not only extract the latest version of the file snapshot, but also completely mirrors the original code repository. It has the following advantages: a. Since every extraction oper
git remote operation——multiple remote repositories for one project
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:131 Category:Git
-
Multiple remote repositories for a git project In our git project, the command to operate the remote repository information is $ git remote # 查看当前所有的远程仓库的名称 $ git remote -v # 查看远程仓库的名称和远程仓
Git cherry pick command usage
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:190 Category:Git
-
git cherry-pick is a powerful command that allows us to select an arbitrary Git commit by reference and attach it to the HEAD of the current working branch. Cherry picking is the act of picking a commit from one branch and applying it to an
Comparison between Git merge and Git rebase
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:171 Category:Git
-
The git rebase command may seem like Git wizardry to beginners, but if used carefully, it can actually make life easier for your development team. In this article, we compare git rebase with the related git merge command and identify all th
How to fix Git error Error: src refspec master does not match any
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:124 Category:Git
-
When using Git, we may encounter the error "src refspace master does not match any". Here's what the error means and how to fix it. What does src refspec master does not match any Mean in Git mean? We may encounter this error when we try to
Rebase local branch when pulling changes from remote repository branch in Git
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:144 Category:Git
-
This article will cover the basics of rebasing your local branch when pulling changes from a remote repository branch in Git. We use the version control system Git to track changes made to files. We commit changes in a local branch in our l
Undo Git Stash
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:187 Category:Git
-
This article explains how to make and save changes to a repository. Git allows you to save changes locally and push them to a server when needed. In Git, we don't use the term save , but commit . We use git add , git commit , and git stash
View a list of cache entries in Git
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:59 Category:Git
-
We often need to pause our work and focus on something else in our development environment. Therefore, we may need to temporarily save our current work and focus on a different one. We may want to resume our original work later. git stash T
Git stores specific files
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:115 Category:Git
-
This article will cover storing changes to only specific files in Git. In Git, when we make some changes in our working tree, we may have some changes which may or may not be staged in our local repo. We may now wish to save these changes f

