Adapter vs Decorator vs Facade vs Proxy Design Pattern in Java
There are some striking similarities between the Adapter, Decorator, Facade, and Proxy design patterns as they all use composition and delegation to solve problems. The Adapter pattern wraps an interface and delegates calls to it. Decorator wraps an object and implements behavior on it, Facade wraps one or more interfaces to provide an easy to use central interface, and the Proxy pattern also wraps a Subject and delegates calls to it. So the question is, why are there different patterns? What is the difference between the Adapter, Decorator, Facade, or Proxy patterns if their structure is the same. The answer is 目的. Yes, all of these Java design patterns have similar structures and class diagrams, but their purposes are completely different.
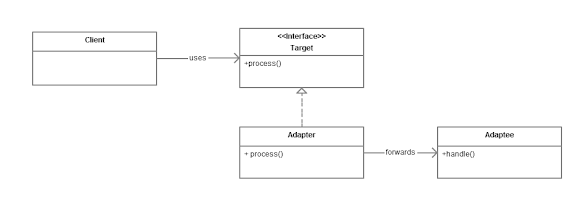
- The main purpose of the Adapter pattern is to convert interfaces. The Adapter pattern lets two components work together that would not work because of incompatible interfaces.
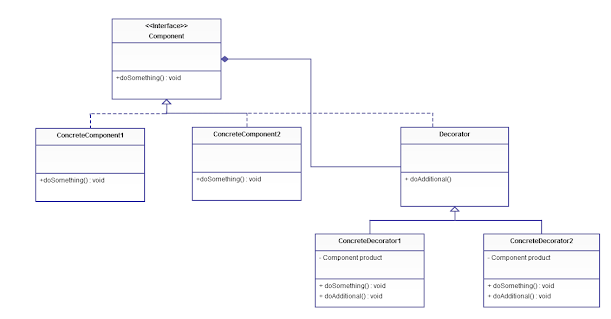
- The Decorator pattern adds new functionality at runtime. It allows us to enrich an object even after it is created.
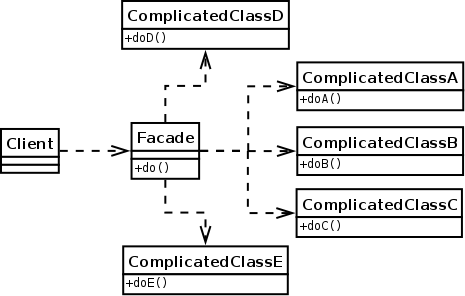
- The facade design pattern neither converts the interface nor adds new functions, but only provides a simpler interface. Therefore, instead of directly accessing the various components of the system, the client uses the facade. The facade design pattern allows the client to interact with a complex system with a simpler interface and less work. The facade will then call the various components.
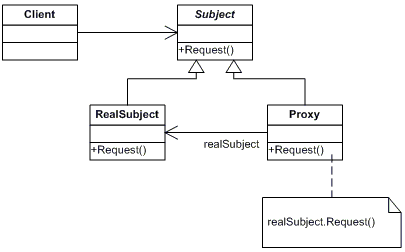
- The proxy pattern is also very similar to the adapter and decorator, but its purpose is to control access to an object. The proxy prevents the client from accessing the object directly, but instead acts as a real object that can provide alternative behavior or forward requests to the original object.
Proxy is the most general pattern among all these patterns and it can be used in different ways like remote proxy for communicating with remote objects, virtual proxy for controlling access to expensive objects, protection proxy for providing access to objects based on role , caching proxy which can return cached objects etc.
Similarities between Adapter, Facade, Proxy and Decorator patterns in Java
One of the main similarities is the structure, all these patterns wrap an object and delegate request processing or method calls to them. There is something else here, which is the commonality between all these patterns.
- In classic design patterns, they are all defined as structural patterns, such as GOF design patterns.
- They all use composition and delegation to achieve their intentions. Adapter uses composition to forward calls from target interface to adaptee interface, Decorator also uses the same technique before adding new behavior, Facade is composed of all subcomponents, Proxy also uses composition and delegation to forward requests.
- Both Decorator and Proxy patterns are meant to stay in place of the original object, that is why both Decorator and Proxy patterns implement the interface of the real object. Due to this nature, decorators and proxies can be passed to methods that accept the original or real object.
- Adapter and Facade patterns forward the request to a different interface which can be an adapter or any component interface from the subsystem.
- Another similarity between the Adapter and Facade patterns is that they can wrap multiple interfaces, which is also different from the Decorator and Proxy patterns because they tend to operate on one object.
Difference between Adapter vs Decorator vs Proxy vs Facade design pattern in Java
Now that we know there are a lot of similarities between all of these structural patterns, let's look at some of the differences between them. As I said before, they differ in their intent, the problems they solve, and where they are used.
- The Adapter pattern converts interfaces, the Decorator pattern does not convert interfaces, it just implements the interface of the original object so that it can be passed to a method that accepts the original object. The Facade and Proxy patterns also do not convert interfaces.
- One of the main differences between the Decorator and Proxy patterns is that a Decorator never creates an object, it always adds new functionality on an already existing object, a Proxy on the other hand can create an object that doesn't exist. It can stand in for a real object until it's ready and then start forwarding requests to it.
- The decorator design pattern also allows adding multiple functionalities and can do so in an ordered manner by chaining multiple decorators , whereas the proxy pattern does not suggest proxy chaining.
- If we compare Decorator and Facade patterns then you can see that unlike Decorator, Facade does not add any new behavior, it simply calls an existing method from the interface, which it provides as a facade.
- Unlike the Decorator, Proxy, and Adapter design patterns, the Facade does not need to implement any specific interface. In fact, the Facade can even be a class that simply holds the various subsystem components and provides simpler operations required by the client, and then calls the corresponding methods on the subsystem.
For example, we can think of Car as a facade that provides the start and stop start()methods stop(). When the client calls start()the method, it may start various subsystems by calling corresponding methods, such as engine.start(), wheels.move(), lights.on(), ac.on()and so on.
UML diagrams for Adapter, Decorator, Proxy, and Facade patterns
The similarities we have been talking about are even more evident in their structure. If you look at their UML diagrams, you can clearly see the similarities.
UML diagram of the adapter pattern
UML diagram of the decorator pattern
UML diagram of the proxy pattern
UML diagram of the Facade pattern
That’s the difference between Adapter , Decorator , Proxy , and Facade design patterns in Java . Knowing the similarities and differences between them will improve your knowledge and ability to spot the use of design patterns. In short, if you need to convert an interface, use the Adapter design pattern to make the two parties work together.
If you need to hide the real object due to various reasons, then you should use the Proxy design pattern in Java, such as security, performance, networking, etc. Use the Decorator pattern to add new behaviors on the existing objects at runtime, it provides the flexibility to mix behaviors and apply them in different orders as per the client requirements.
Finally, the facade pattern is used to provide clients with simplified access to complex systems. The facade provides a higher level of abstraction and should contain the operations required by the client.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Store Div Id in PHP variable and pass it to JavaScript
Publish Date:2025/04/13 Views:51 Category:PHP
-
This article shows you how to div id store a in a PHP variable and pass it to JavaScript code. We will answer the following questions. What is div id ? How to div id store in a PHP variable? How to pass variables to JavaScript code? Let’s
Use of Linux command at - set time to execute command only once
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:158 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
This article mainly involves a knowledge point, which is the atd service. Similar to this service is the crond service. The functions of these two services can be similar to the two functional functions of javascript. Those who have learned
Design Patterns in Java - Visitor Pattern
Publish Date:2025/03/19 Views:175 Category:ALGORITHM
-
Today, we are going to learn one of the most useful patterns, the Visitor Pattern. What is the Visitor pattern? Well, let's look at an example. Let's say you're a software engineer working at a university. The university rarely has establis
How to use Strategy Pattern in Java?
Publish Date:2025/03/19 Views:142 Category:ALGORITHM
-
Hi everyone, you might have heard, “Can you tell me about any design pattern other than Singleton design pattern that you have used recently in your project?”. This is one of the popular questions in various Java interviews in recent ye
Difference between Proxy Mode and State Mode in Java
Publish Date:2025/03/19 Views:76 Category:ALGORITHM
-
Hi guys, if you are preparing for Java interview and looking for difference between Proxy and State design pattern, then you are at the right place. In the past, I have explained several important object-oriented design patterns like State,
Strategy Design Pattern and Open-Closed Principle in Java
Publish Date:2025/03/19 Views:114 Category:ALGORITHM
-
The Strategy design pattern is based on the Open/Closed design principle , the famous " O SOLID " of design principles . It is one of the patterns that has become popular in the field of object-oriented analysis and design, along with the D
How to implement binary search in Java without recursion?
Publish Date:2025/03/19 Views:198 Category:ALGORITHM
-
Hey Java programmers, if you want to implement binary search in Java and looking for iterative and recursive binary search algorithms, then you have come to the right place. Today I am going to teach you an important algorithm. In computer
How to implement the singleton pattern in JavaScript ES6+
Publish Date:2025/03/19 Views:55 Category:ALGORITHM
-
In this article, we will show you how to implement the singleton pattern in JavaScript. If we are a full-stack JavaScript developer, we know that JavaScript is a powerful language and we can build amazing websites with it. On the other hand
How to use the Adapter design pattern in Java
Publish Date:2025/03/19 Views:77 Category:ALGORITHM
-
The Adapter design pattern in Java , also known as the Wrapper pattern, is another very useful GOF pattern that helps bridge the gap between two classes in Java. According to the Gang of Four pattern list, Adapter is a structural pattern, m

